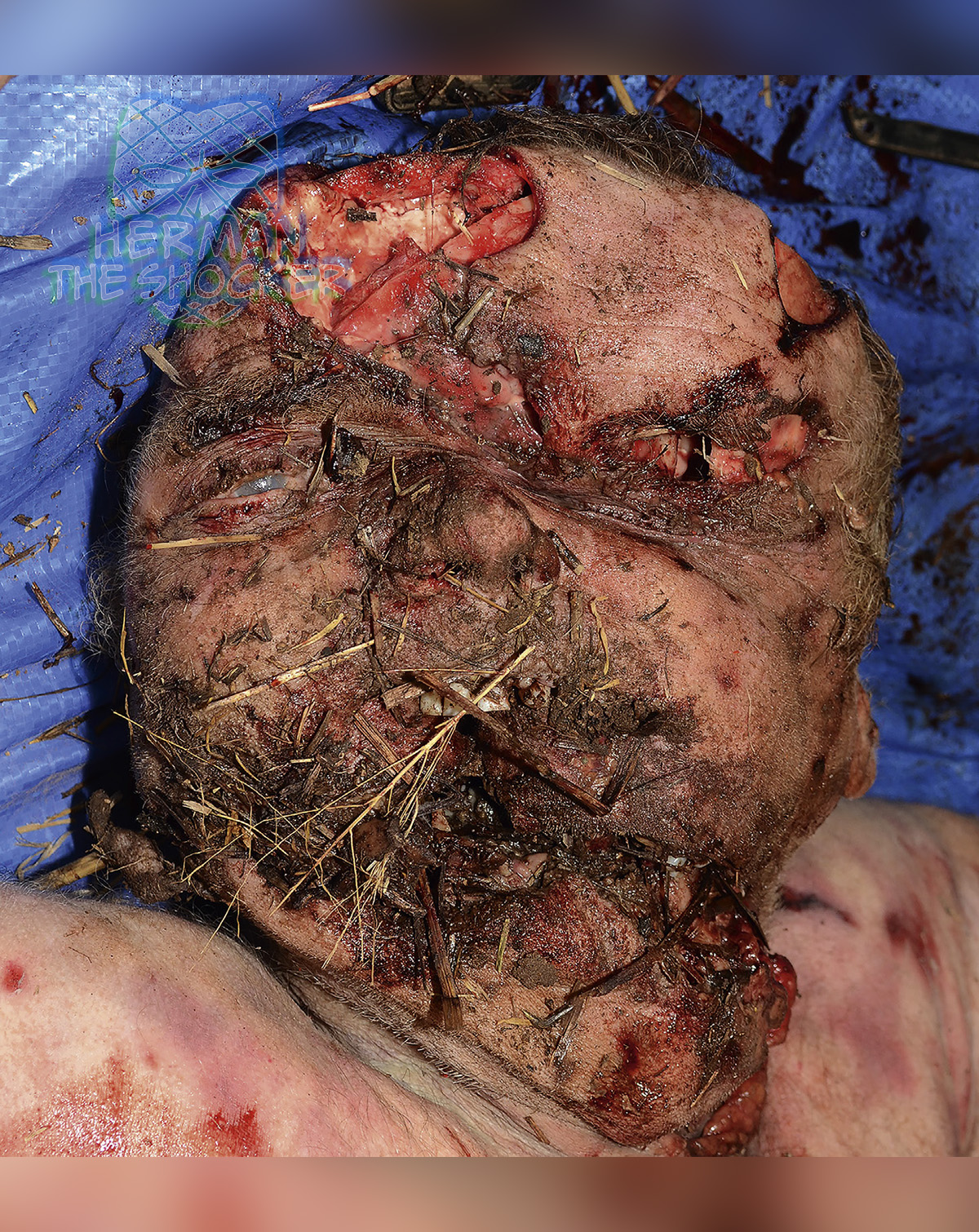
An elderly male pilot was flying a microlight aircraft with one middle-aged male passenger in the rear of the aircraft. When preparing to land, one wing dipped and the aircraft dived straight into the ground. The pilot was ejected and was located lying 2 m (6.5 ft) from the aircraft. The passenger was located in his seat. The cause of death for both the pilot and the passenger was from multiple injuries sustained in a light-plane accident.
Pilot: There were extensive abrasions over the body and large lacerations on the posterior part of the left and right legs. There was comminuted compound fracturing of the cranial vault with extrusion of cerebral contents. There were extensive lacerations to the face with compound fracturing of the maxilla, nasal bones, and mandible. There was blood in the left and right external auditory canals, nostrils, and mouth. In addition to the skull, there were multiple fractures involving the cervical and thoracic spine, pelvis, bilateral ribs, larynx, and bones of upper and lower limbs. There was also extensive damage to the internal viscera with lacerations to the heart, lungs, liver, and spleen.
Passenger: There were multiple abrasions over the body and a large laceration on the posterior aspect of the left thigh and the perineal region. There was blood in the left and right external auditory canals, nostrils, and mouth associated with dental damage. There were multiple, palpable rib fractures. There was a compound fracture of the left humerus and a closed fracture of the right radius and ulna.
Severe injuries may be associated with the ejection of an individual from the relative protective confines of an aircraft cabin. Ejection injuries may be associated with the flailing of limbs resulting in extensive lacerations. Postmortem CT images of the passenger showed extensive fractures of the frontal and nasal bones, maxilla, mandible, and zygomas and multiple fractures of the left parietal and temporal bones, and a fracture of the right temporal bone.
The post-cranial skeleton also showed multiple bilateral fractures of the ribs, fractures of the left ilium and separation of the pubic symphyses, a comminuted fracture of the midshaft of the left femur, a compound fracture of the distal left humerus, a fracture of the midshaft of the left ulna and fractures of the midshafts of the right ulna and radius. Postmortem CT images of the pilot showed extensive anterior and lateral disruption of the skull and post-cranial skeleton. It is interesting to note the differences between the skeletal trauma seen in the passenger compared with that seen in the pilot. In this accident, these differences may relate to the fact that the pilot was ejected.
Latest posts