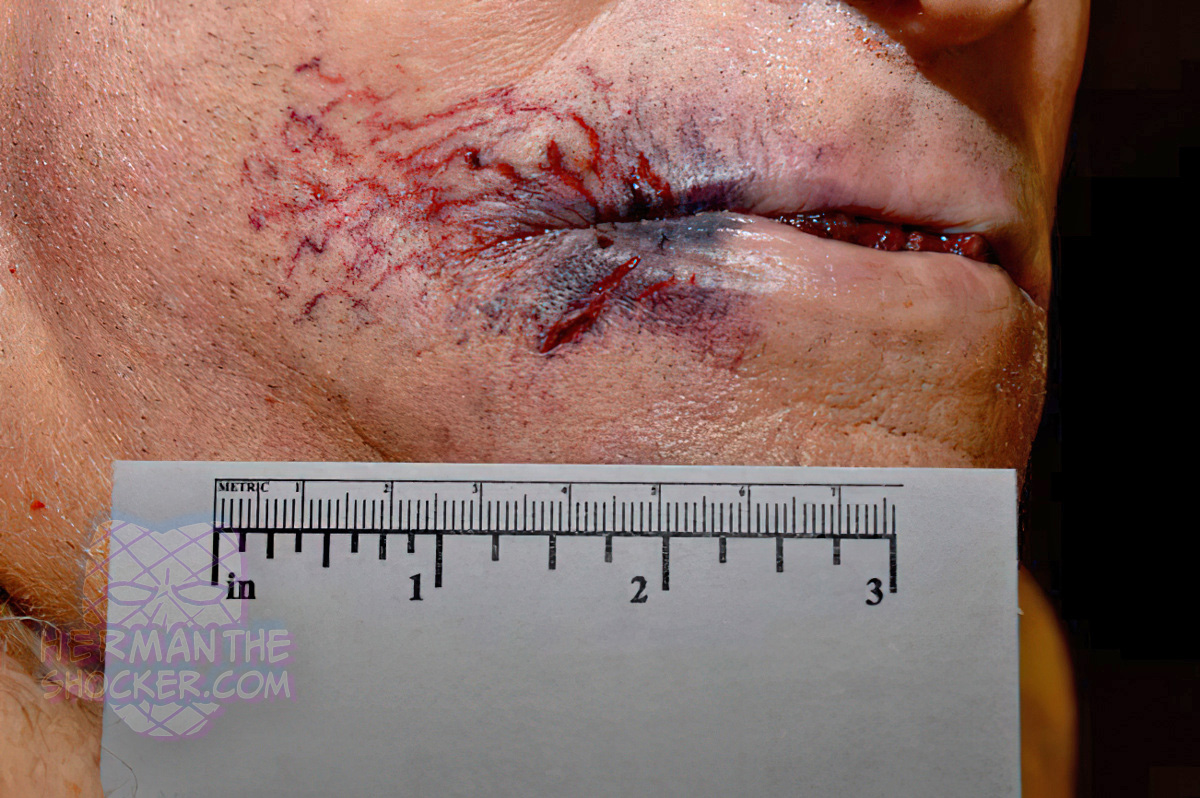
Perioral lacerations from an intraoral gunshot wound blowback from a closed mouth. In this intraoral gunshot wound, note the tissue tears extending from the side of the mouth. These tears result from the large amount of gases exiting the end of the barrel at high pressures. In contrast to the head, contact shotgun wounds of the torso often have a fairly innocuous appearance, likely related to the elastic nature of the tissues of the body walls and the ability of the chest or abdominal cavities to be able to accommodate a large amount of expelled gas.
The discharge of a weapon involves the release not only of a projectile but of hot gas under high pressure as well. If the lips are sealed around the barrel, the rapid expansion of departed gases causes the cheeks and face to balloon far beyond their elastic capacity. This results in the characteristic tears seen in the figure.
Latest posts