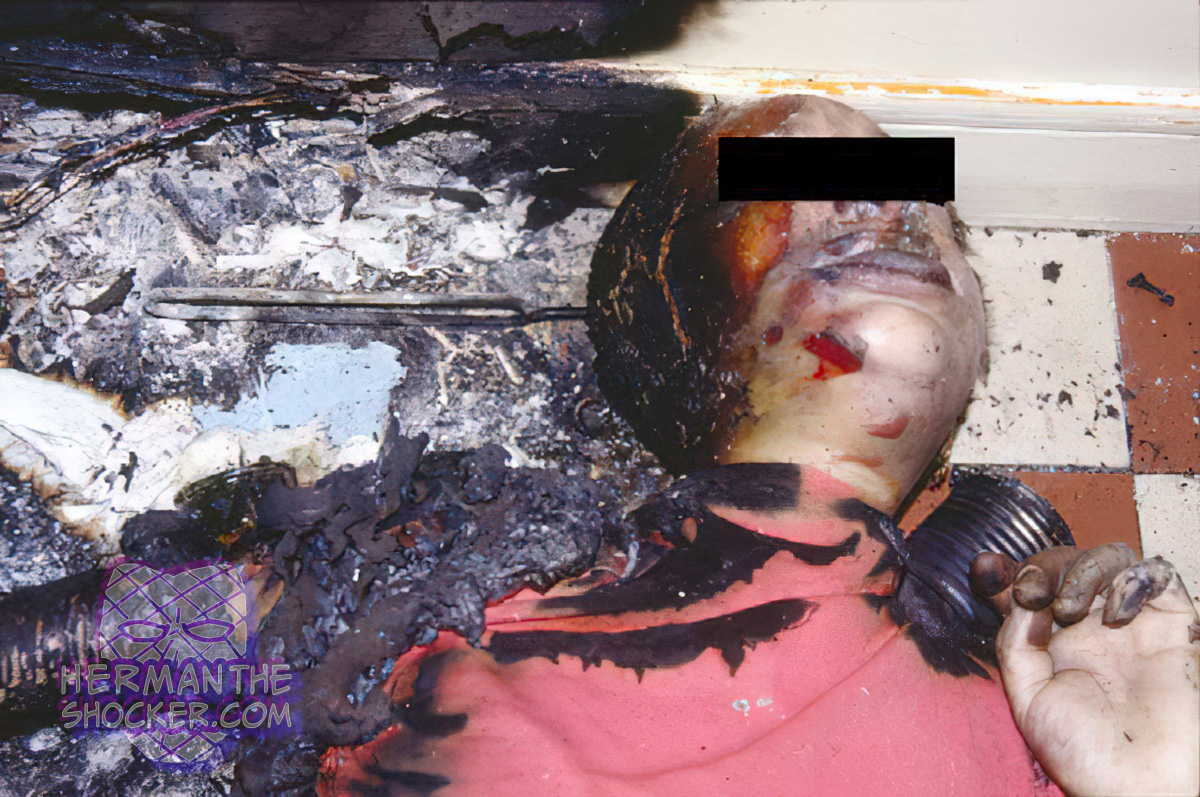
A fatal case of burns by flash fire which caused the death of a 41-year-old woman when she used an air-freshener spray in a kitchen. Burning with flash fire on the left side of the skull, face, neck, and shoulder. Fires in confined spaces such as a room can produce a phenomenon called a flashover, often involving a gas heater or device. Once a fire starts, it produces radiant heat, hot gases, and smoke. Initially, the fire and hot gases begin to heat the ceiling and adjacent upper walls and then objects in the lower portion of the room. In turn, the combustible materials in the room begin to give off flammable gases.
Adults may also be involved in accidents caused by the flammability of many aerosol cosmetics and household products; this can be attributed to the use of hydrocarbon propellants in combination with alcohol solvents. Products such as hairspray, deodorants, air fresheners, bug bombs, tire sealant, solvents, paints, and cleaners are propeled out of their aero- sol gases, many of which contain propane, butane, isopropane, or isobutane. All these common products can generate dense, flammable vapors, creating a path for fire or explosion. When vapors spread throughout an enclosed space, they are subsequently ignited by an ignition source, and an explosion or flash fire may result. The aerosol propellant gas consisted of a mixture of propane and butane and was ignited by the flame of a gas heater. Ignition resulted in a flash fire, extensively burning the woman.
Latest posts