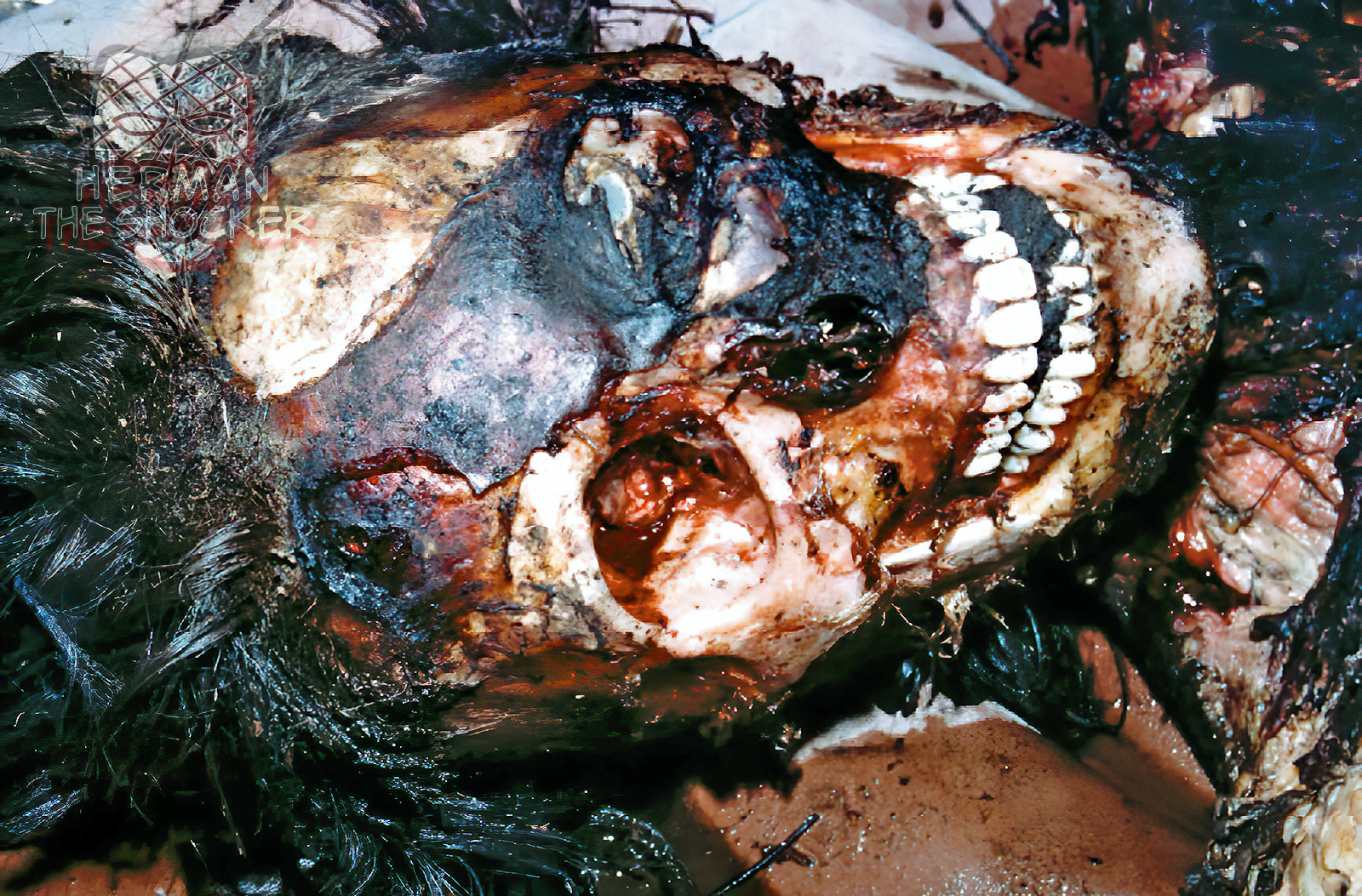
In this particular case, the badly charred and burned remains of the victim of a kidnapping, rape, and murder were found in a wooded area. Although the authorities believed they had found the missing victim, they would require the services of a forensic odontologist to assist in providing positive identification based on dental records.
Dentition provides an excellent means of identification, especially when antemortem records and x-rays of the deceased are available for comparison. Forensic odontology—the scientific application of dentistry to legal matters—has become a viable asset to the law enforcement community. Today, many forensic odontologists are trained to respond to the needs of law enforcement officers, the legal profession, and forensic pathologists.
Practically speaking, in cases where the remains have been badly mutilated or burned, are in advanced putrefaction, or have been submerged in water for a long period of time, the possibility of obtaining any fingerprints of value is quite remote. This is where the forensic odontologist can be of assistance. Using powerful cameras, x-rays, and medical records, he or she can, through examination of the dentition and jawbones of the deceased, provide the investigator with positive identification as well as bite-mark identification. In addition, the forensic odontologist can provide information about the deceased, including age, general facial characteristics, race, socioeconomic group, occupation, or habits.
The eruption of teeth in the human body is a relatively predictable process during the early years of growth. The forensic odontologist can provide a rather accurate estimate of the ages of persons under 14. The first teeth, referred to as baby teeth or deciduous teeth, make their appearance from 7 months to 2 years. The loss of these baby teeth and the eruption of the first permanent molars begin at approximately 5 years of age and continue into the early teens.
The forensic odontologist relies on the wear patterns for victims past age 14. As a general rule, the older a person becomes, the more his or her teeth show evidence of wear, dental repair, and gum recession. Using microscopic and radiological (x-ray) examination of dentition, the forensic odontologist can estimate the age of an adult within 5 years’ accuracy. Estimates of age for the prepubertal child can be calculated within 6 months by examining the stage of development of the permanent tooth buds.
Latest posts