Germany. A young, initially unidentified female was found dead in public on a snowy winter day. She was found in a ditch next to the side of a road. Numerous severe injuries, partially involving smooth wound margins, were grouped on the head and both hands. During the scene investigation, accidental injuries (such as injuries caused by a rotary snow plough) or homicidal injuries (such as placing the head in a milling cutter with body dumping) were raised as possible differentials. Subsequent identification revealed the deceased worked at a landfill site in close proximity to the place where she was found.
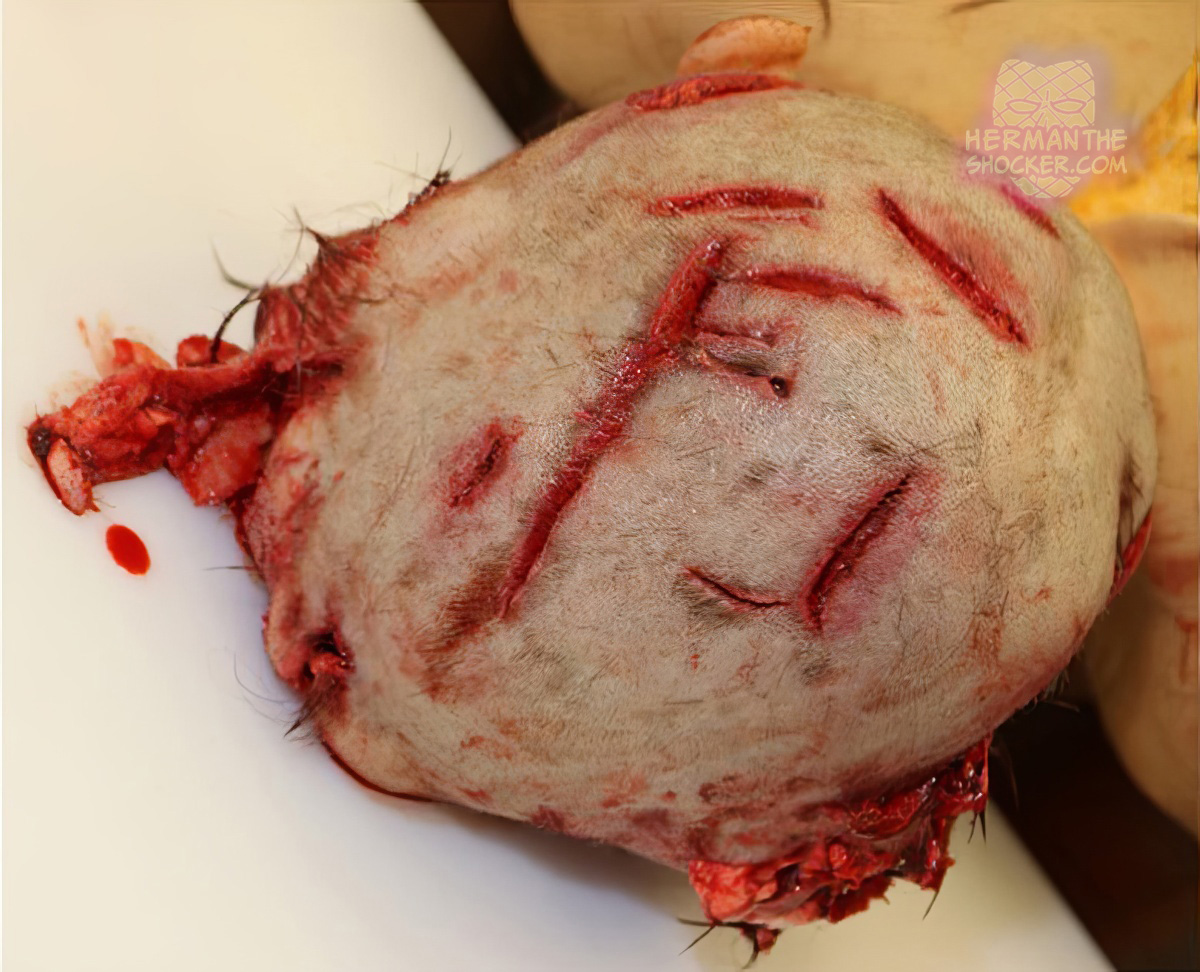
During forensic autopsy, the head was found to have more than 40 chop injuries grouped in three regions; the crown and occipital region, the left ear region, and the face. These injuries were associated with localized skull fractures and severe osseous destruction of the midface. The wound characteristics were typical for axe injuries. Additionally, some bruises were observed next to the chop wounds. The fingers on both hands had chop injuries in a typical active and passive defense-type injury distribution. Toxicological analysis performed on blood and urine samples were negative for alcohol and commonly screened drugs. The cause of death was traumatic open brain injury with partial brain laceration by an axe-like implement, and the manner of death was homicide. No crime scene evidence was found at the work place of the deceased. However, no conclusion could be made regarding the exact shape or type of the implement that caused the injuries.
This murder case was solved when the police located a dead suspect in an apartment with suicidal notes. An axe-like meat cleaver with blood spots and hair on the cutting edge was found next to him. After dactyloscopic and genetic investigations, this implement was superimposed with the injuries on the female skull and showed perfect matches. Several impact injuries were visualized, and it was concluded that the injuries were caused by a combination of slashing and blunt force of the meat cleaver.
It was concluded that the female victim was able to react to the assault, highlighted by many defense injuries on her hands. Ultimately, the head injuries resulted in fatal head injury with a survival interval of just minutes. This was supported by microscopic wound age estimation on representative samples of injured skin.
Latest posts