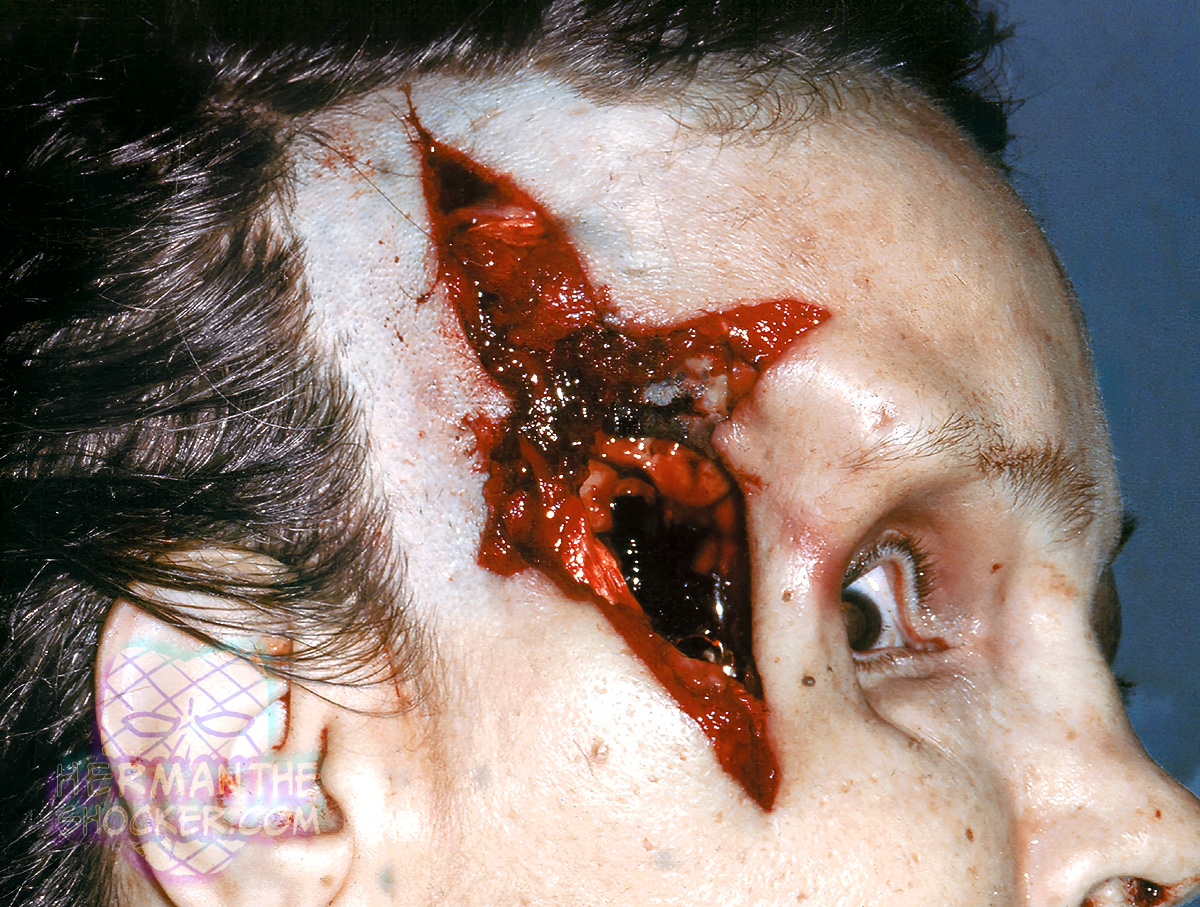
This 52-year-old woman has a contact gunshot wound of her right temple. Note how the scalp is split by tears radiating from a central region of the wound where the end of the muzzle of the gun was pressed tightly against the skin. When a gun is fired, a cloud of hot gas is expressed from the end of the muzzle along with the projectile. In a contact gunshot wound of the head, these gases are forced between the scalp and the cranial bones and build up pressure along its path. The pressure is eventually released as the scalp tears.
Scalp injuries (the most common of which are contusions, abrasions, and lacerations) are of particular importance because they provide information about the type, location, and severity of force applied to the head. Careful examination and documentation of the presence or absence of injury is a vital component of forensic casework. Never consider photographs to be an unnecessary expense. Even when they illustrate a paucity or complete lack of findings (pertinent negative), they have the potential to make or break a case.
Latest posts